Fourier : DFT
La transformée de Fourier est une fonction qui représente la densité spectrale d’un signal initial. Cette transformée de Fourier joue donc un rôle fondamental pour l’analyse des harmoniques d’un signal.
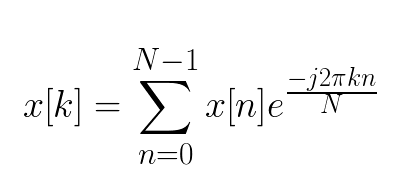 </img>
</img>
function dft_C(x) {
let X = [];
const N = x.length;
for (let k = 0; k < N; k++) {
let sum = new Complex(0, 0);
for (let a = 0; a < N; a++) {
const Phi = (TWO_PI * k * a) / N;
const c = new Complex(cos(Phi), -sin(Phi));
sum.add(x[a].mul(c));
}
sum.re = sum.re / N;
sum.im = sum.im / N;
let amp = sum.amplitude();
let phase = sum.phase();
let freq = k;
X[k] = {
re: sum.re,
im: sum.im,
freq,
amp,
phase
};
}
return X;
}Pour permettre de travailler dans le monde des Complexeson ajoute la Classsuivante :
class Complex {
constructor(re, im) {
this.re = re;
this.im = im;
}
mul(c,ret) {
const re = this.re * c.re - this.im * c.im;
const im = this.re * c.im + this.im * c.re;
ret.re = re;
ret.im = im;
return ret;
}
add(c, ret) {
ret.re = this.re + c.re;
ret.im = this.im + c.im;
return ret;
}
sub(c, ret) {
ret.re = this.re - c.re;
ret.im = this.im - c.im;
return ret;
}
mult(a) {
this.re *= a;
this.im *= a;
}
amplitude() {
return sqrt(this.re * this.re + this.im * this.im);
}
phase() {
return atan2(this.im, this.re);
}
}